Globalization is probably the most debated topic in contemporary global market in recent decades and the use of the term grew exponentially as the planet braced to welcome twenty first century. First half of the first decade of the new century saw the launch Thomas L. Friedman’s book on globalization named “The World is flat”. He argued that the connectivity had lead the businesses to be powerful. He has contended that every company in the globe are at the ‘level playing field’ metaphoric of the word ‘flat’. Thus he suggests that every company operating in today’s competitive world along with countries and individuals requires a change in order to survive or be prepared to be swept by the incessant waves of globalization. In opposition, Pankaj Ghemawat counter argues that the idea presented by Friedman is based on hunch rather than on the logical ground.
This critical analysis on contradicting perspectives of International business strategy is the outcome of intense study of books, journals, articles, videos and several other mediums undertaken over the past few months. Written by an American Journalist and weekly columnist at New York Times, Thomas L. Friedman, “The world is flat” depicted the global scenario of business activities being performed around the globe in late 1990s and early 2000s and categorized them under three phase Globalization 1.0, Globalization 2.0 and Globalization 3.0. Discussing the ten important factors responsible for flattening of the world, Friedman was wary of the fact that this flattening could actually impede USA economically thus suggesting the remedies. But is globalization surely making the world flat? Not everybody thinks so. Though the book received number of awards and is indeed a bestseller, many critics slammed the argument including Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz and global strategist and economist Pankaj Ghemawat.
A very few people would disagree that the world today is extremely globalized. Business today have been so simpler that boundaries between the countries have become absolutely obsolete. But is the world really flat that the geographical boundaries are utterly irrelevant?
In the bestseller book “the world is flat”, Thomas L. Friedman ingeniously described the next phase of globalization. The argument made by Friedman may be valid as he have portrayed several situations and examples during his travel abroad and conversation with several business as well as non-business people. The conclusion made by Friedman in the book urges government, organizations and individuals to be wary of the dynamic world and stay ahead of the trends that are most likely to cause shift in the way things is being done today in order to stay competitive in the global marketplace. Several evidences discussed in the book that have caused the world to be flattened may or may not be relevant now as the pace of technological change has surpassed the previous predictions regarding the future. Moreover, Friedman even discussed about the forces and challenges that could hinder the pace of flattening of the world citing the threat of Al-Qaeda. Times have changed by now and Al-Qaeda exert minimal threats in the today’s global scenario, but the threat of terrorism still exists from newer and fresher groups. ISIL has been the major threats to every developed nation now with some deadly attacks still fresh in the memory, latest being the Paris Attack.
As the final pages of the book approaches, Friedman discusses about “the Dell theory of conflict prevention” wherein he argues that the two countries are less likely to go to war if they have invested in the business together and are thus being the part of same global supply chain. Friedman even suggests that the forces which helped the world to get flattened could even work the other way round. Citing the example of the upgrade in the technology, he advocates that technology is unable to get us protected and it is us who should control and decide how to make the best use out of it.
There is no arguing to the fact that this age is of globalization and the companies, countries or even individuals failing to be compatible with it are bound to fail sooner or later. But is the world globalized to the extent that it has become flat and the companies all around the globe are fairly placed at the same level? What is the degree of the globalization? Has the globalization reached saturation that there seems no relevance of the physical boundaries? The answer is not fairly simple. Soon after the book released, it gained fair proportion of the acclaims critically. The Washington Post in 2005 termed the book an “engrossing tour” and an “enthralling read”. Warren Bass (2005), quoted that “We’ve no real idea how the 21st century’s history will unfold, but this terrifically stimulating book will certainly inspire readers to start thinking it all through”, in the book review published In the Washington Post.
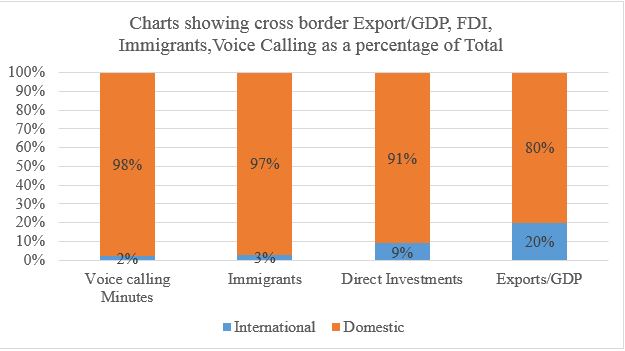
But it was criticism which fueled the debate of whether the world is actually flat. Joseph E. Stiglitz (2007) in his famous book “Making globalization work” argued that despite the radical amendment in the global landscape, not only the world was not flat, in fact in many facets the world was getting less flat. This was just the beginning and was followed by several other criticism. Professor of London School of Economics, John Gray (2005), counter argued the notion made by Friedman that globalization makes the world peaceful and free. The criticism didn’t end that soon rather took up the pace. Presenting his idea with the abundance of the data and facts, Pankaj Ghemawat (2007), in the article published in Foreign Policy magazine opposed the viewpoint of the Friedman saying only a fraction of the globalization we ponder actually exists in reality. He very precisely cites the example saying 90% total internet traffics, total investments, and all phone calls remains within the national boarder and even suggests that the level of globalization which is roughly around 10% could still slip away. He argues that even though global economic and financial hubs like New York, London, Frankfurt, and Hong Kong are well interconnected they are found to have been concentrated very much on domestic activity despite the platform. Arguing that the perfect representation of the globalization is FDI, and when looked upon to the total fixed investment made, less than 10% of the investment has actually crossed the border slamming the mantra “Investment knows no boundaries” as argued by globalization champion, metaphoric of Friedman. Other several interesting facts presented by Pankaj includes the long term migration which stood 3% in 1900s is <3% now as presented in figure 2 below. Google, considered as most globalized website have less than 30% of market share in Russia in search engines, the biggest complication for google to operate in Russia is the complexity of the Russian language. Pankaj in his article in Foreign Policy seems to have analyzed all the possible factors representative of the globalization consisting cross-border migration, telephone calls, management research and education, private charitable giving, patenting, stock investment, and trade, as a fraction of gross domestic product (GDP) have found that all of the above is closer to 10% rather than 100%. Thus, called this the “10 Percent Presumption.”
Though the World have become a small marketplace as of result of development in sophisticated technology and huge numbers of barriers has been eliminated, the distances still matters. The impact of distance is identified and assessed by the use of CAGE framework discovered by Pankaj Ghemawat. More the distance between the two countries in different dimensions of the CAGE framework, riskier it is to do the business. Culture, Administration, Geographic, Economic distance are the dimension of the framework. Idea of globalization is abysmal and more complex as it portrays the hue of iceberg. Globalization is the multifaceted and façade, thus presenting the surficial appearance. Though Friedman was partially right on the argument he made, the geographical, historical, administrative, cultural, economic distances has always relevance and cannot be ignored. No matter the level of globalization, national boundaries can never go obsolete let alone at today’s extent of globalization. Conventional globalization definitions refer to interdependence and interconnectedness of economies, but as the time passes the definition becomes even more complex as several factor must be taken into consideration. Both the parties have valid point to make the argument, in fact these extremes at the either end are the seemingly contradicting perspectives of International Business strategy. One can only conclude that the globalization is the factor that have made the world a single marketplace but the degree of globalization is not the one that we have assumed it to be. Thinking global and being globalized is not bad per se, but to think that the world has flattened and that national boundaries are irrelevance could be an overstatement unless and until it is backed by the reasonable data.
Globalization is an inevitable force. Those organization aspiring to grow must consider the fact that the pace of change taking place in business market is very rapid globally. Every big companies wants to go global to increase their presence worldwide and further growth potential. But it is easier said than done. The world is not globalized to the extent that we are made to believe, in fact we have been made to believe the exaggerated situation of globalization. This is what Pankaj Ghemawat argues in the criticism of the Thomas L. Friedman’s “the world is flat”. The level of globalization is still very amateur, even though if it was to the extent Friedman have suggested distances still matter. Several trade theories put across over the centuries have never considered the distance factor, even till date it has been ignored. Even Michael porter have failed to address the issue in his diamond theory of national competitive advantage. But trade is all about the distances and globalization can never eliminate the physical distances and other distances as argued by Ghemawat in the CAGE framework.
History doesn’t lies, what has happened in the past acts as the roadmap of the future. The recent past trends are likely to continue and drastic change is least expected except in the field of Science and technology. Every aspects that reminds us of globalization when looked closely upon gives us the clear picture as to the extent of globalization. Facebook for example is a global social network with users around the globe, but when we observe it more closely we find that the level of interaction internationally is less than 15%. So the presented extent of the globalization is way much more than the existing level of globalization.
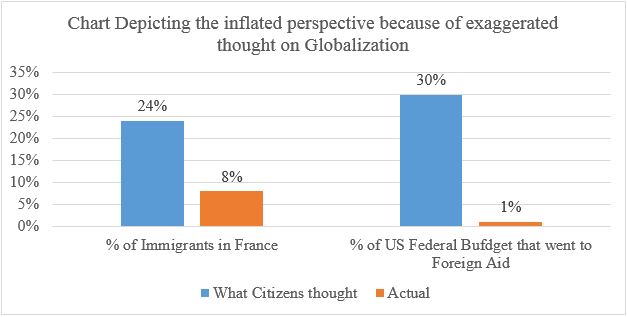
The exaggerated presentation of the extent of globalization seems to have great impact on the individual perspectives which Ghemawat discusses in the TED Talk through some recent researches. Citizens of France tends to think that their country accounts for about 24% of the immigrant population which is in fact 8% of the total population. Also American citizen when asked about the percentage of their federal budget that went to foreign aid answered very close to 30%, which in fact is 1% as depicted in the figure 1 above. This suggests that exaggerated presentation of any ideas without the solid backing of the data and figures leads to the overestimation and inflated view about the matter which in turn might lead to the making up the bad decisions on these grounds.

